Welded Wire Mesh vs Square Wire Mesh: Strength, Uses & Applications Explained
In cities rising with steel and glass, across quiet pastures dotted with grazing livestock, and inside humming industrial plants where automation never sleeps—two unassuming materials are shaping the modern world: welded wire mesh and square wire mesh. They fence our spaces, reinforce our buildings, and carry products through production lines. Yet despite their similar appearance, these grids speak vastly different engineering languages. One is forged by precision welding; the other woven like fabric from metal threads. Understanding their differences isn’t just technical—it’s essential to choosing durability over disappointment.
From Raw Steel to Structured Grid: The Making of Two Meshes

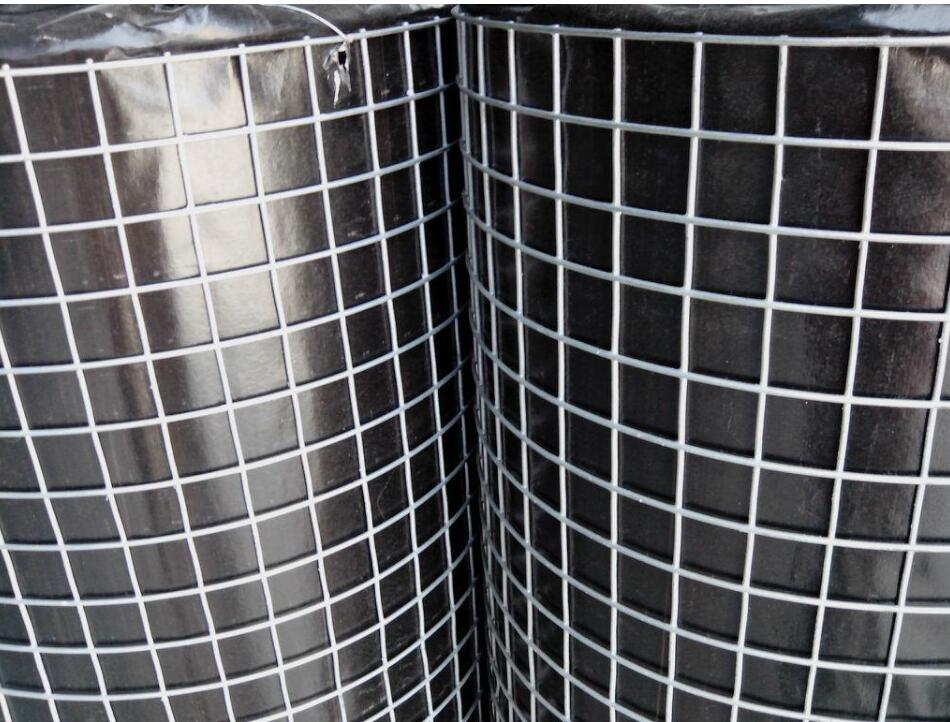
The journey of welded wire mesh begins with cold-drawn steel wires laid perpendicular to each other. At every intersection, a burst of electrical current fuses them together through resistance welding—a process that creates rigid, immovable joints. This “point-anchoring” method results in a grid that resists deformation under load, behaving much like a skeleton with locked joints. It's this structural predictability that makes it ideal for applications demanding dimensional stability.
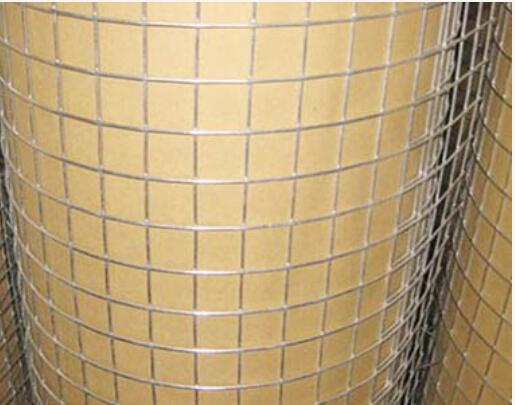
Square wire mesh, on the other hand, follows an older tradition—textile logic applied to metal. Woven on specialized looms, parallel wires interlace over and under at right angles, creating a uniform checkerboard pattern. There’s no fusion at the crossings; instead, integrity comes from tension and weave tightness. The result? A mesh with subtle flexibility, capable of absorbing minor shocks without breaking. Think of it as chainmail armor—strong yet slightly yielding when pressed.
Battle of Strength: Rigidity vs Resilience Under Pressure
When force meets form, the contrast becomes clear. Welded wire mesh excels in compressive strength and long-term load-bearing scenarios. Its fused nodes prevent slippage, making it less likely to distort under sustained weight—critical in concrete reinforcement or heavy-duty flooring. Imagine a warehouse floor enduring daily forklift traffic; here, welded mesh acts as a steadfast internal framework, distributing stress evenly and preventing cracks.
Square wire mesh shines where some give is beneficial. In fencing applications, especially for animal enclosures, its slight elasticity helps absorb impact from animals pushing against it. While not as rigid, its continuous weave provides excellent tensile strength along both axes. Over time, this can translate into fewer failures at connection points, particularly in dynamic environments exposed to wind, movement, or vibration.
Where Each Mesh Rules: Real-World Applications Across Industries

In construction sites worldwide, welded wire mesh has become the go-to choice for reinforcing concrete slabs, driveways, and foundations. Placed before pouring, it controls cracking caused by shrinkage and thermal changes. Contractors value its flat profile and consistent spacing, which ensure even distribution of strength throughout the structure.
Farmers and ranchers, meanwhile, often prefer square wire mesh for perimeter fencing. Available in various aperture sizes, it allows customization based on livestock type—small openings keep chickens secure, while larger ones suit cattle. When combined with high-tensile steel and galvanized coating, it withstands years of exposure to rain, snow, and soil corrosion.
Inside factories, welded mesh panels serve as durable conveyor belts or machine guards, supporting heavy components in automotive or manufacturing workflows. Conversely, in greenhouses and aviaries, square mesh provides optimal airflow and light penetration while keeping pests out and plants or birds safely contained.
Beyond Dimensions: Decoding Material Choices and Finishes
Selecting the right mesh isn’t just about shape—it’s about chemistry and coating. Galvanization, either hot-dipped or electro-coated, remains the gold standard for rust protection, especially in outdoor settings. For even greater longevity, PVC-coated variants offer enhanced resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation—perfect for coastal installations or corrosive industrial atmospheres.
Wire gauge (thickness) and mesh count (number of openings per inch) further refine performance. Thicker wires increase load capacity but reduce flexibility; higher mesh counts create finer barriers, useful in security screens or small-animal housing. Matching these specs to your environment ensures optimal function and lifespan.
The Hidden Cost Equation: Upfront Price vs Lifetime Value
While square wire mesh may appear more economical initially, mismatched use can lead to costly repairs. Using non-welded mesh in high-stress concrete applications might save pennies today but risk structural compromise tomorrow. Conversely, over-specifying welded mesh for lightweight fencing inflates costs unnecessarily. Smart selection balances initial investment with maintenance frequency, expected service life, and total cost of ownership.
Toward Smarter, Greener Grids: The Future of Wire Mesh
As sustainable construction and smart agriculture gain momentum, both meshes are evolving. High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels reduce material use while boosting performance. Modular pre-assembled panels cut installation time and waste. And because both types are fully recyclable, they align well with circular economy goals.


